
Why Invest In Malaysia?

Are you seeking a dynamic and deep market with diverse opportunities and strong growth potential?
Looking for a vibrant economy that offers both portfolio diversification and long-term returns?
Malaysia brings all this together, making it the ideal gateway to Southeast Asia’s thriving markets.
6 Reasons to Invest
01
Malaysia as a Reformer
02
Strong Economic Fundamentals
03
Policy Driven
04
Mature Financial Market
05
Stable Regulatory Environment & Governance
06
Dedication to Sustainability
Malaysia as a Reformer
Strong Economic Fundamentals
Policy Driven
Mature Financial Market
Stable Regulatory Environment & Governance
Dedication to Sustainability
Reason 01
Our commitment to economic reforms
Malaysia's economic journey is a testament to its resilience and adaptability, offering significant benefits to domestic and global investors.
Over the past few decades, Malaysia has transformed from a primarily commodity-based economy to a well-diversified economy which consists of various high-complexity industries. This transformation reflects the country's strategic planning and robust policy reforms, which have not only spurred domestic growth but also provided investors with a stable and conducive environment for long-term capital appreciation.
Propelling Malaysia forward
In the 1960s and 1970s, Malaysia's economy was heavily reliant on commodities such as rubber and tin. The industrialisation of the economy in the 1980s characterised its restructuring towards becoming export-driven, catalysed by the strong Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) inflows during the period. This saw annual economic growth rates exceeding 9%, driven by sectors such as electronics, textiles and palm oil.
By the 2000s, Malaysia reformed further, transitioning towards a services-oriented economy. Services, which encompass finance, tourism, and information technology, gradually became a major contributor to the country's GDP, representing more than half of the economy by 2023.
This shift attracted significant foreign portfolio investments, particularly in equities and bonds. Malaysia's capital markets have become a key destination for foreign portfolio investors, with more than 20% of Malaysian Government securities (MGS) and Malaysian Government Investment Issues (MGII) being held by foreign investors.
In recent years, Malaysia has continued to undertake efforts to deepen and develop its financial markets. Among these efforts include expanding the bond and sukuk markets to be among the largest in ASEAN, while strengthening the regulatory framework to ensure greater market transparency. The modernisation of financial market infrastructure, along with initiatives to enhance liquidity and broaden market participation—has helped ensure that Malaysia’s capital markets remain robust, resilient, and globally accessible. These efforts have positioned Malaysia as a key financial hub in the region.
Shaping the future
Our policy priorities have remained flexible to adapt to the evolving dynamics of the global economic landscape. To this end, Malaysia has introduced future proof policy frameworks that are designed to attract and support foreign investors while advancing its economic ambitions.
- The Ekonomi MADANI Framework, launched in 2023, aims to identify Malaysia’s inherent strengths and create new opportunities ahead with a strong emphasis on execution. The intended goal of ‘raising the ceiling’ will be achieved by regionalising our businesses, transforming the economy and increasing national competitiveness. With a strong focus on innovation, sustainability, and strategic investments, Malaysia welcomes foreign participation in the nation’s growth as it drives its economy to become a leading force among Asian markets.
- The National Energy Transition Roadmap (NETR) emphasises sustainable growth through a shift towards renewable energy and green technologies. This initiative aligns with Malaysia's commitment to achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.
- Additionally, the New Industrial Master Plan 2030 (NIMP 2030) was also introduced to transform the manufacturing and manufacturing-related services sectors, building on emerging global trends. This seven-year plan for industrial development is centred around a mission-based approach and fosters dynamic collaboration between the Government and the private sector.
Reason 02
Strong economic fundamentals
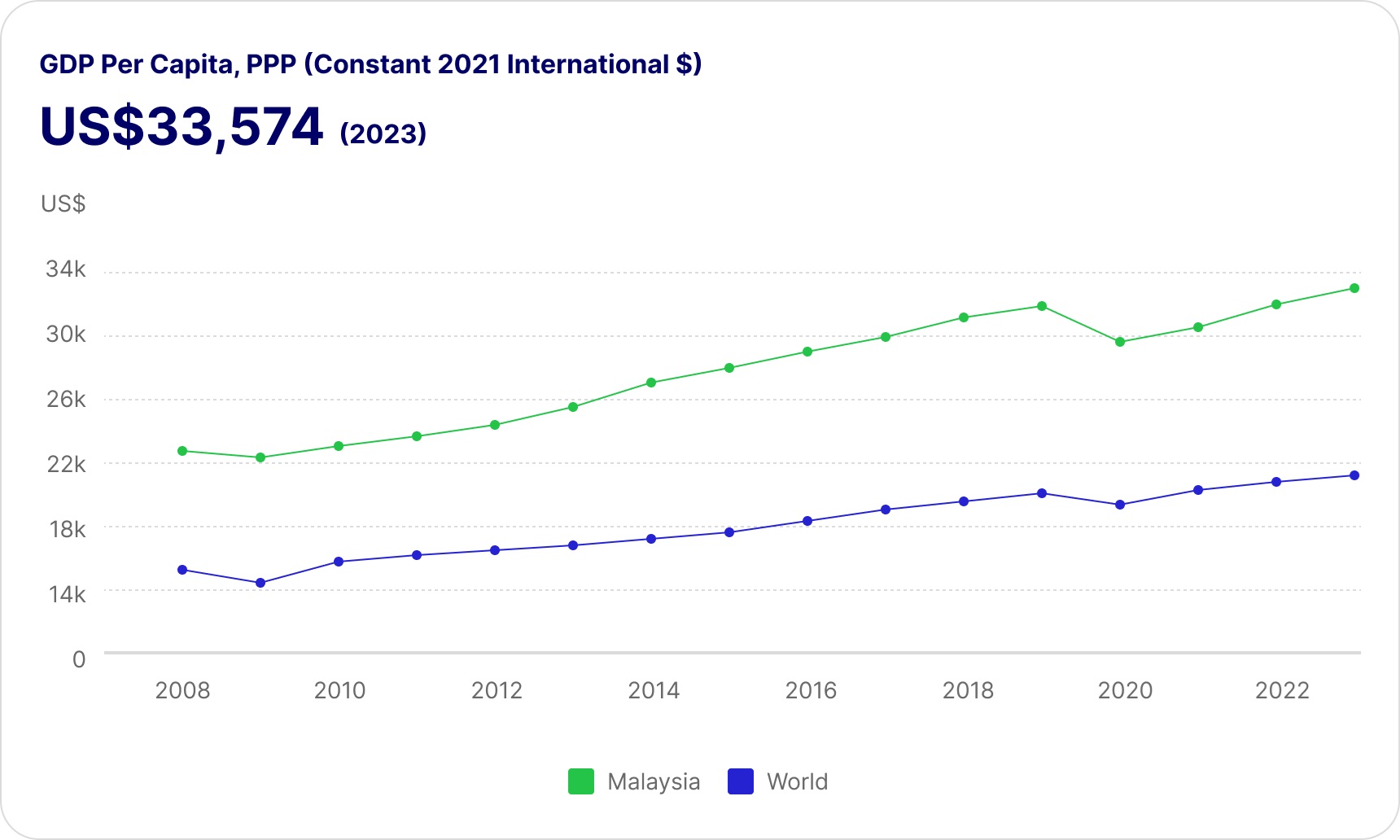
Malaysia's economic achievements are built on strong fundamentals that have driven resilience and sustained growth over the years. These fundamentals, including steady GDP growth, a continuous current account surplus, and a commitment to sound fiscal and monetary policy, form the backbone of the country's economic stability.
For foreign investors, this creates a favourable investment environment. The steady GDP growth signals a healthy, expanding economy with rising business opportunities and a growing consumer base, while the continuous current account surplus reflects Malaysia's robust export performance. These key factors ensure a stable inflow of foreign exchange, reduce external vulnerabilities and boost investor confidence.


Continuous current account surplus
Malaysia's robust external position is demonstrated by its continuous current account surplus, a steadfast characteristic of its economy, indicative of strong export performance. Its strategic role as a global trading hub, a diversified export portfolio, and robust supply chain network especially in electronics and commodities-related industries, have facilitated a healthy external trade position.
As a small open economy, Malaysia’s expansive trade network is facilitated by key trade agreements with global partners, amongst others:
- Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP): As one of the 15 signatories to the RCEP, Malaysia is part of the world’s largest free trade agreement. With the RCEP countries being key trading partners for Malaysia, it is set to improve investment facilitation and post-investment support, creating more growth opportunities.
- Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP): This agreement positions Malaysia strategically and enhances its competitiveness on the global stage by granting access to new markets such as Canada, Mexico, and Peru, expanding its reach beyond existing free trade agreements.
For more information on existing trade agreements entered by Malaysia, please visit the Ministry of Trade, Investment and Industry’s website on Malaysia’s Free Trade Agreements.
Reason 03
Strong institutional capacity
Malaysia's economic trajectory and financial markets have been shaped by a series of well-crafted policies aimed at ensuring stability, fostering growth, and driving innovation. These policies reflect the strength of Malaysia’s institutional capacity, providing a solid foundation for sustainable development.
Deliberate structural reforms
Malaysia's economy has seen various transformations, driven by structural reforms focused on enhancing competitiveness, diversifying the economy base, and improving productivity. The Government’s commitment to infrastructure development, human capital investment, and digital transformation has been central to propelling Malaysia’s economic growth.
At the cornerstone of these reforms are the five-year Malaysia Plans (Rancangan Malaysia). Introduced in 1996, these plans guide national economic development, ensuring that policies remain robust and adaptable to an ever-changing global economy. Each iteration of the Malaysia Plan underscores the country’s commitment to transparent, future-ready economic policies that support long-term growth.
Steadfast commitment to fiscal reforms
The Government's prudent fiscal policies manifest in responsible Government spending and effective debt management, all of which ensure the sustainability of public finances.
Malaysia's fiscal policy is guided by comprehensive and forward-looking plans that aim to balance its role in supporting growth with fiscal prudence. The Medium-Term Fiscal Framework (MTFF) outlines the Government's plan on fiscal consolidation which supported by measures to diversify and broadening the revenue base, optimising expenditure as well as enhancing fiscal governance.

Malaysia's commitment to prudent fiscal management
The Public Finance and Fiscal Responsibility Act 2023 (FRA) was introduced to improve the legal framework for public finance and complement the Financial Procedure Act 1957. The FRA encompasses fiscal principles aimed at ensuring macroeconomic stability, achieving and maintaining a prudent debt level and establishing effective fiscal risk management. In this regard, the Legislature has set the following targets:
- Annual development expenditure of at least 3% as a percentage of gross domestic product (GDP);
- Fiscal balance of -3% or less as a percentage of GDP;
- Debt level at 60% or less as a percentage of GDP; and
- Financial guarantees not exceeding 25% as a percentage of GDP
These measures are expected to strengthen public finances and support long-term fiscal sustainability.
Monetary Stability
One of the hallmarks of Malaysia's economic management is its ability to maintain low and stable inflation. Through the prudent conduct of monetary policy, Bank Negara Malaysia (Central Bank of Malaysia) ensures that inflation remains low and stable, fostering an environment conducive to a sustainable economic growth.
Reason 04
Vibrant financial markets
Malaysia’s financial markets are among the most advanced in Southeast Asia, offering investors access to a deep, well-developed, and liquid market. As of 1H 2024, the domestic bond and sukuk markets, valued at over RM2 trillion are the largest in ASEAN, driven by both Government and corporate issuances.
Bursa Malaysia, the country’s stock exchange, also boasts a market capitalisation exceeding RM2 trillion. The foreign exchange market, with an average daily turnover of USD17 billion during the same period, is highly liquid and easily accessible through the licenced onshore banks and their global networks of Appointed Overseas Offices (AOO).
Key elements of Malaysia's financial markets:
- Robust financial system
Malaysia’s financial system features strong banking groups with a presence in ASEAN and beyond. These banking groups are well-capitalised and able to support investors with a wide suite of financial products and derivatives. As of end 2023, the total Malaysian banking system assets amount to RM3.5 trillion.
For a comprehensive list of Malaysia’s financial sector participants, please visit Bank Negara Malaysia’s Financial Sector Participants Directory.
- Diverse asset classes
Malaysia offers a wide range of investment opportunities across various investment products including equities, bonds (both conventional and Islamic Sukuk), derivatives, amongst others. This broad spectrum of financial instruments reflects the depth and sophistication of the market. Further information about these different asset classes may be found here.
- Vibrant stock market
Bursa Malaysia, is one of the largest and most developed bourses in Southeast Asia, with a substantial market capitalisation (1H2024: RM2 trillion) and a wide range of listed companies across various sectors. In 2023, Bursa Malaysia remained a focal point for foreign institutional investors, who made up 29.2% of the securities market's Average Daily Trading Value (ADV), an increase from 26.8% in 2022.
The benchmark FBMKLCI has steadily been improving in line developments within the global financial market, rising more than 12% year-to-date in October 2024. The year 2023 also saw 32 companies opt for IPOs on Bursa Malaysia, raising RM3.6 billion and contributing RM13.6 billion to total market capitalisation.
- Liquidity and Accessibility
The Malaysian financial markets boast considerable liquidity, especially in the Government and corporate bond/sukuk sectors (1H2024: RM2 trillion), which rank among the largest in the region. The accessibility to these markets, coupled with Malaysia's favourable economic outlook, enhances their appeal and positions them as an attractive destination for investment.
Key elements of Malaysia's financial markets:
- Robust financial system
Malaysia’s financial system features strong banking groups with a presence in ASEAN and beyond. These banking groups are well-capitalised and able to support investors with a wide suite of financial products and derivatives. As of end 2023, the total Malaysian banking system assets amount to RM3.5 trillion.
For a comprehensive list of Malaysia’s financial sector participants, please visit Bank Negara Malaysia’s Financial Sector Participants Directory.
- Diverse asset classes
Malaysia offers a wide range of investment opportunities across various investment products including equities, bonds (both conventional and Islamic Sukuk), derivatives, amongst others. This broad spectrum of financial instruments reflects the depth and sophistication of the market. Further information about these different asset classes may be found here.
- Vibrant stock market
Bursa Malaysia, is one of the largest and most developed bourses in Southeast Asia, with a substantial market capitalisation (1H2024: RM2 trillion) and a wide range of listed companies across various sectors. In 2023, Bursa Malaysia remained a focal point for foreign institutional investors, who made up 29.2% of the securities market's Average Daily Trading Value (ADV), an increase from 26.8% in 2022.
The benchmark FBMKLCI has steadily been improving in line developments within the global financial market, rising more than 12% year-to-date in October 2024. The year 2023 also saw 32 companies opt for IPOs on Bursa Malaysia, raising RM3.6 billion and contributing RM13.6 billion to total market capitalisation.
- Liquidity and Accessibility
The Malaysian financial markets boast considerable liquidity, especially in the Government and corporate bond/sukuk sectors (1H2024: RM2 trillion), which rank among the largest in the region. The accessibility to these markets, coupled with Malaysia's favourable economic outlook, enhances their appeal and positions them as an attractive destination for investment.
Global Islamic Financial Hub
Malaysia is globally recognised as a leading hub for Islamic finance, a position it has built through decades of strategic development and innovation. The country has a comprehensive Islamic financial system that includes Islamic banking, Takaful (Islamic insurance) and Islamic capital markets.
Malaysia's Shariah-compliant financial products and services are highly regarded for their adherence to Islamic principles, attracting investors from around the world seeking ethical and socially responsible investment options.
Read more about Malaysia’s Islamic financial market here.
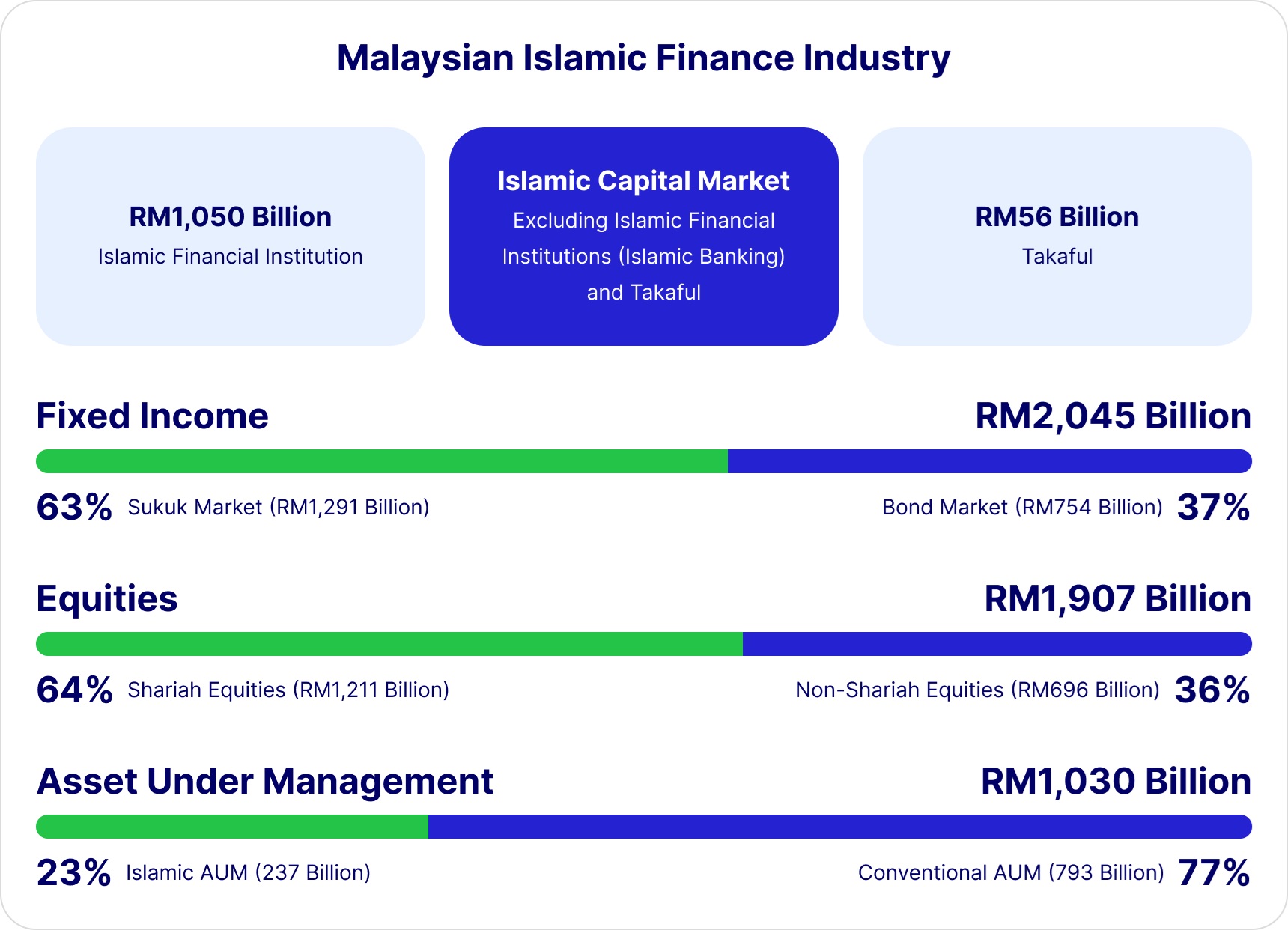
Source: Bursa Malaysia via GFIEF2024
Commitment to elevating Malaysia's Islamic finance industry
Institutions such as Bank Negara Malaysia, the Securities Commission Malaysia and the Malaysian International Islamic Financial Centre (MIFC) play pivotal roles in promoting and regulating the Islamic finance industry.
The presence of prominent local and foreign Islamic financial institutions and the country's commitment to continuous innovation and regulatory excellence ensure that Malaysia remains at the forefront of the global Islamic finance industry, thereby providing more opportunities to investors seeking to add Shariah-compliant assets in their portfolio.
Commitment to elevating Malaysia's Islamic finance industry
Institutions such as Bank Negara Malaysia, the Securities Commission Malaysia and the Malaysian International Islamic Financial Centre (MIFC) play pivotal roles in promoting and regulating the Islamic finance industry.
The presence of prominent local and foreign Islamic financial institutions and the country's commitment to continuous innovation and regulatory excellence ensure that Malaysia remains at the forefront of the global Islamic finance industry, thereby providing more opportunities to investors seeking to add Shariah-compliant assets in their portfolio.
Reason 05
Stable Regulatory Environment & Governance
Malaysia's regulatory environment has been carefully designed to promote stability, and effectiveness. Our regulatory framework is underpinned by a robust governance system and proactive economic policies that stimulate economic growth and orderly intermediation of financial activities, which collectively foster a conducive business environment for investment activities within the country.
The following are regulatory bodies that are key in ensuring orderly function of our markets:
The FSA governs the broader financial services sector and works in tandem with the CMSA to regulate investment related financial activities.
IFSA regulates Islamic financial institutions and products ensuring they comply with Shariah principles.
This act is the primary legal framework governing the activities of the capital markets providing the foundation for investor protection and market transparency.
The FSA governs the broader financial services sector and works in tandem with the CMSA to regulate investment related financial activities.
IFSA regulates Islamic financial institutions and products ensuring they comply with Shariah principles.
This act is the primary legal framework governing the activities of the capital markets providing the foundation for investor protection and market transparency.
Corporate Governance and Compliance
- Malaysia's corporate governance framework
Malaysian Code on Corporate Governance (MCCG) ensures that listed companies adhere to internationally recognised practices of corporate governance.
- Shariah compliance
Malaysia has a well-developed Islamic capital market, with the Securities Commission Malaysia overseeing Shariah-compliant financial products, including Islamic bonds (Sukuk) and equity through its Shariah Advisory Council (SAC). For Islamic financial institutions, The Shariah Advisory Council of Bank Negara Malaysia plays a vital role in ensuring end-to-end Shariah compliance.
Reason 06
Dedication to Sustainability
Malaysia's commitment to sustainability is a key factor that enhances its attractiveness to foreign investors. The Malaysian Government has undertaken numerous initiatives to promote sustainable development, adopting a holistic approach to economic growth that integrates environmental, social and governance (ESG) considerations.
Malaysia is supportive of the United Nations (UN) agenda on Sustainable Development Goals (SDG). Its commitment to all 17 SDG’s is overseen by the National SDG Council, which ensures ESG considerations are embedded within national-level policy frameworks.



Comprehensive regulatory framework
The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environmental Sustainability and the Malaysian Green Technology and Climate Change Centre (MGTC) ensure compliance with environmental standards and the promotion of eco-friendly practices. The Joint Committee on Climate Change (JC3) also acts as a bridge between regulators and industry in pursuing collaborative actions for building climate resilience within the Malaysia financial sector.

Comprehensive regulatory framework
The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environmental Sustainability and the Malaysian Green Technology and Climate Change Centre (MGTC) ensure compliance with environmental standards and the promotion of eco-friendly practices. The Joint Committee on Climate Change (JC3) also acts as a bridge between regulators and industry in pursuing collaborative actions for building climate resilience within the Malaysia financial sector.

To learn more about the Joint Committee on Climate Change (JC3) click here.
Get Started
Explore our resources and guides for more information.






